What is Urea & Why Is it Important for Athletes?
1 min read
Published on
May 22, 2025
Written by
EDGE
Share this article
What Is Urea?
Urea is a waste product formed from the breakdown of protein. It’s filtered by the kidneys and is a useful indicator of hydration, training load, and protein metabolism in athletes.
High levels can signal dehydration or muscle breakdown. Low levels may suggest under-fuelling or poor protein intake.

"Urea is a byproduct of protein metabolism and a helpful marker of training stress and hydration. Elevated levels may indicate muscle breakdown or dehydration, particularly in endurance athletes. I recommend testing urea monthly during high-volume phases and pairing it with creatinine and creatine kinase to monitor overall metabolic strain and recovery status"
What are normal urea levels for athletes?
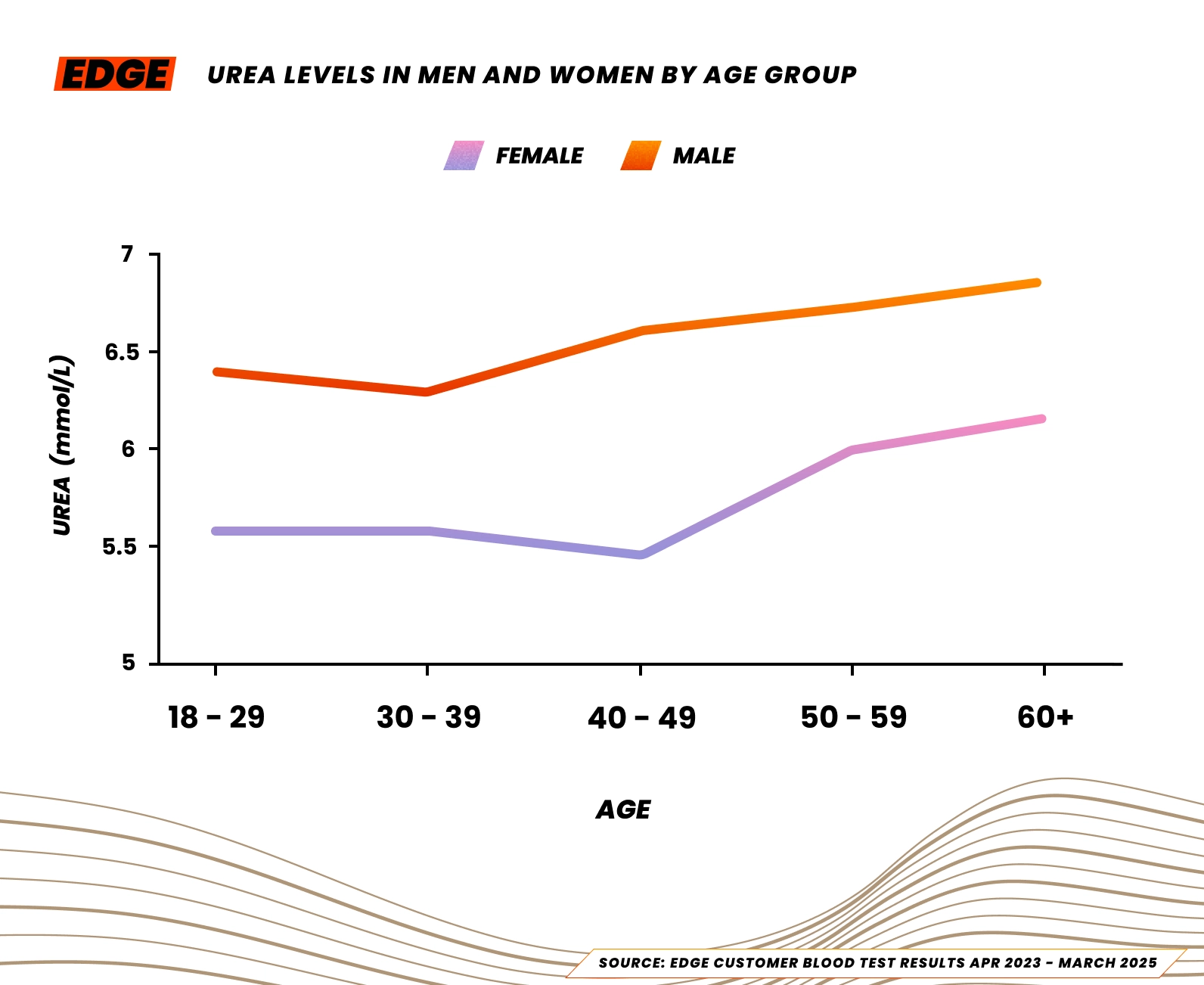
We looked at blood test data from EDGE customers and found the median urea levels for women are 5.6 mmol/L and 6.6 mmol/L for men.
Here is a breakdown of urea levels by age:
| Table 1: Urea Levels in Men and Women by Age Group (mmol/L) | ||
| Age Group | Female | Male |
| 18-29 | 5.6 | 6.4 |
| 30-39 | 5.6 | 6.3 |
| 40-49 | 5.4 | 6.6 |
| 50-59 | 6 | 6.7 |
| 60+ | 6.2 | 6.8 |
Source: EDGE customer blood test results Apr 2023 – March 2025.
The labs we used to analyse blood samples state a healthy range for urea is generally between 2.5-7.8 mmol/L.
Why Urea is Important for Athletes
-
Recovery Monitoring
Elevated urea can suggest incomplete recovery, especially when combined with high creatinine or CK.
-
Hydration Status
Urea levels rise with dehydration, valuable for athletes training in heat or for long durations.
-
Protein Utilisation
Helps assess whether protein intake matches training demands.
Why Test Urea?
Urea is an indicator of protein metabolism and training stress, offering valuable insight into how well your body is coping with physical load. It’s especially useful to test:
-
During intense training or competition blocks
-
If signs of dehydration, fatigue, or muscle soreness persist
-
To monitor recovery in conjunction with creatinine and CK
In Summary
-
Urea tracks recovery, hydration, and protein metabolism
-
High = dehydration or overtraining; low = under-fuelling
-
Best interpreted alongside creatinine, eGFR, and CK
Check Your Urea Levels
Check and monitor your urea levels from home with our sports blood tests.
Get 10% off your first order
Want regular tips on how to make the most of your results? Join our newsletter and we'll give you 10% off your order!
Get the knowledge
Get expert advice to help you improve your results.
Go to our knowledge center


