What is Triiodothyronine (T3) & Why Is it Important for Athletes?
1 min read
Published on
May 22, 2025
Written by
EDGE
Share this article
What Is Free T3?
Free T3 is the active form of thyroid hormone, directly responsible for regulating metabolism, energy use, and thermogenesis. It’s converted from T4 and is the most metabolically powerful thyroid hormone.
Athletes with disrupted T3 levels may struggle with recovery, fatigue, and poor adaptation to training.

"Free T3 is the active form of thyroid hormone and a sensitive marker of metabolic slowdown, often affected by under-fuelling or stress. I recommend testing T3 in conjunction with TSH and free T4, especially if you're noticing fatigue, poor recovery, or unexplained weight changes. Monitoring thyroid function every 6–12 months can help optimise training outcomes."
What are normal Triiodothyronine (T3) levels for athletes?
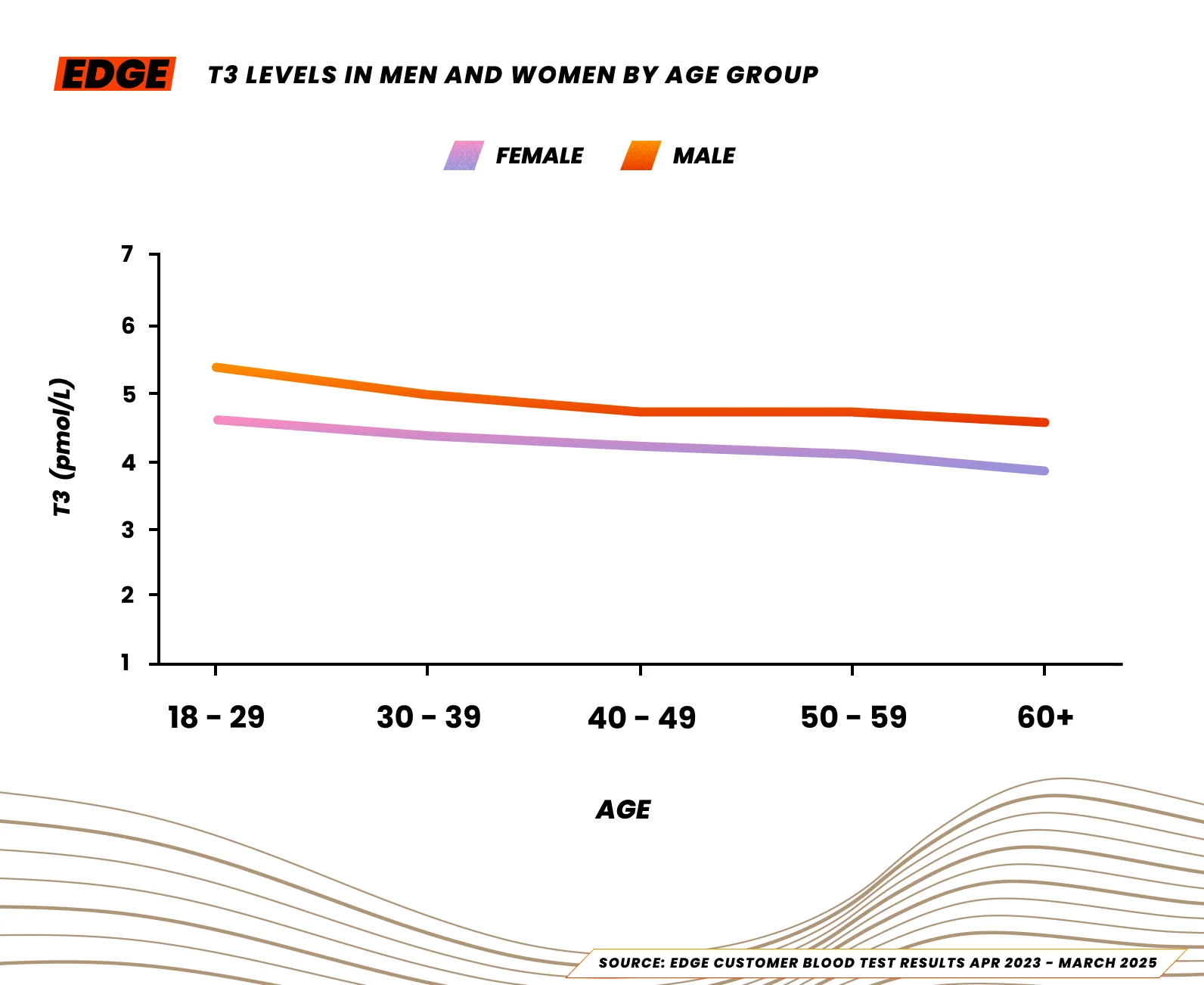
We looked at blood test data from EDGE customers and found the median triiodothyronine levels for women are 4.4 pmol/L and 4.9 pmol/L for men.
Here is a breakdown of Triiodothyronine (T3) levels by age:
| Table 1: T3 Levels in Men and Women by Age Group (pmol/L) | ||
| Age Group | Female | Male |
| 18-29 | 4.6 | 5.4 |
| 30-39 | 4.4 | 5 |
| 40-49 | 4.3 | 4.8 |
| 50-59 | 4.1 | 4.8 |
| 60+ | 3.9 | 4.6 |
Source: EDGE customer blood test results Apr 2023 – March 2025.
The labs we used to analyse blood samples state a healthy range for Triiodothyronine (T3) is generally between 3.1-6.8 pmol/L.
How T3 Impacts Athletes
-
Energy & Fatigue
Low T3 can leave you feeling tired and cold, even with adequate rest. It can also impair muscle glycogen storage and slow down metabolic efficiency.
-
Training & Recovery
T3 influences protein synthesis and mitochondrial function. Suppressed levels can delay repair and slow aerobic adaptation.
-
RED-S Indicator
Low T3 is a classic sign of relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S) and often appears in athletes who are under-fuelling or overtraining.
Why Test Free T3?
-
To investigate chronic fatigue, low body temperature, or slow recovery
-
As part of a thyroid health check (with TSH and T4)
-
To assess metabolic function in high-volume training blocks
In Summary
-
T3 is your body’s active thyroid hormone, key for energy and metabolic health
-
Low T3 = poor fuelling, overtraining, or RED-S
-
Essential in endurance and body composition sports
Check Your T3 Levels
Check and monitor your T3 levels from home with our sports blood tests.
Get 10% off your first order
Want regular tips on how to make the most of your results? Join our newsletter and we'll give you 10% off your order!
Get the knowledge
Get expert advice to help you improve your results.
Go to our knowledge center


